What is Confidential Computing & Zero-Trust Security?

Introduction
Businesses must rethink their cyber security strategies today. Data breaches, insider threats, and new attack methods happen every day.
Businesses moving to the cloud and edge are shifting sensitive tasks there. Traditional security methods are not enough to protect them. This is where the notion of Confidential Computing and Zero-Trust Security takes place.
Such technologies are rapidly growing to be the staple of enterprise-class data protection. However, what are they, how do they work, and what actions can we take to implement them?
We will explore two important areas: Confidential Computing and Zero-Trust Architecture. These fields help protect your data. They keep your data safe when you store it, during transit, and while you use it.
Confidential Computing What is Confidential Computing?
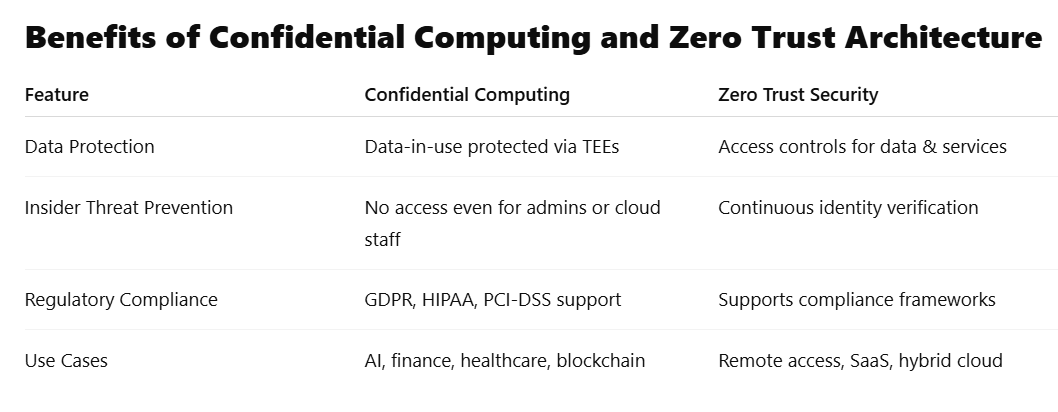
Confidential Computing is a recent cloud-based security solution to data security in processing. Historically, data encryption protects data during transmission or while stored. However, when processing takes place, the system decrypts data and makes it susceptible. That is the gap that Confidential Computing is filling.
It does this by running sensitive tasks in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). This is a secure, hardware-based space. It protects data from unauthorized actions, even from the cloud provider.
Key Features of Confidential Computing:
- Data encrypted at all stages: rest, transit, and use
- Protection against insider threats and malware
- Workload isolation using secure enclaves (TEEs)
- Attestation to verify the integrity of environments
What Is Confidentiality in Computer Security?
In cyber security, confidentiality refers to the protection of information from unauthorized access and disclosure. Confidential computing strengthens this principle by ensuring that:
- Only authorized parties can view or process the data
- The system protects data even while it processes it in real-time memory.
- Privacy and compliance requirements (like GDPR, HIPAA) are maintained
This makes it ideal for sensitive use cases such as:
- Financial data processing
- Healthcare analytics
- AI model training
- Secure edge computing
How Does Confidential Computing Work?
Here’s a breakdown of how confidential computing works in data centers:
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is created by the CPU (e.g., Intel SGX, AMD SEV, ARM TrustZone).
- Applications and data are loaded into the TEE in an encrypted form to get user identity.
- The TEE decrypts and processes the data securely within the enclave.
- No external processes—including the OS, hypervisor, or cloud provider—can access the data inside.
- Remote attestation ensures that the workload runs in a verified, tamper-proof environment.
This technique is especially vital in multi-tenant cloud infrastructures where businesses must ensure data isolation and privacy.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model based on the principle: “Never trust, always verify.”
It assumes that threats can originate from both outside and inside the network. Therefore, no user or system automatically receives trust, even if they exist inside the corporate firewall.
This means:
- Every access request is authenticated, authorized, and encrypted.
- We enforce micro-segmentation and least-privilege principles.
- We apply real-time monitoring and analytics continuously.
What Is Zero Trust in Cyber Security?
In the context of cybersecurity, Zero Trust changes the game. Rather than depending on perimeter defenses like firewalls or VPNs, Zero Trust focuses on:
- Identity-based security
- Device and location validation
- Behavior analysis and anomaly detection
- Continuous verification of access and privileges
This model is very important in today’s world of remote work, BYOD (bring your own device), and cloud apps.
Also Read: What is Cloud Migration? Strategy, Process
How to Implement Zero Trust Security?
Implementing Zero Trust requires a layered approach. Here’s how you can begin:
- Identify Protect Surfaces
Start with defining what needs protection—applications, data, services, assets, and users.
- Map the Transaction Flows
Understand how data flows between users, devices, apps, and networks.
- Create Micro-Segments
Break the network into secure zones with strict access rules using tools like firewalls, SD-WAN, or SASE.
- Enforce Least Privilege Access
Limit user access to only what is necessary using identity and access management (IAM) policies.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Add extra layers of identity verification for both users and devices.
- Continuously Monitor and Improve
Log everything. Use behavioral analytics, threat detection, and machine learning to monitor for anomalies and improve over time.
Ready to Strengthen Your Cybersecurity? Start Here
How to Implement Zero-Trust Security in a Network?
Implementing Zero Trust in a network involves:
- Replacing perimeter-focused security with software-defined perimeters (SDP)
- Deploying cloud access security brokers (CASBs) for SaaS controls
- Using endpoint detection and response (EDR) for real-time threat monitoring
- Utilizing identity providers (IdP) like Azure AD or Okta
- Integrating ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) tools for secure remote access
Why Confidential Computing & Zero Trust Are a Powerful Combo?
Confidential Computing and Zero Trust aren’t mutually exclusive—in fact, they’re complementary:
- Confidential Computing secures the environment where the data is processed.
- Zero Trust secures the access, user, and your network.
Together, they:
- Eliminate blind spots in traditional security
- Safeguard workloads across public, private, and edge clouds
- Mitigate insider threats and supply chain risks
Industry Adoption Examples:
Microsoft Azure Confidential Computing
- TEEs via Intel SGX for secure enclaves
- Supports confidential containers and VMs
Google Cloud Confidential VMs
- Uses AMD SEV for encryption of memory while VMs are running
IBM Cloud Hyper Protect
- Provides FIPS 140-2 Level 4 certified HSM-backed encryption and TEEs
Zscaler, Palo Alto, and Cisco
- Leaders in Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and SASE-based Zero Trust enforcement
FAQs: Confidential Computing & Zero-Trust Security
What is Confidential Computing in simple terms?
This security technology keeps your data safe while you process it. It uses special areas called Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs).
How does Confidential Computing work?
It uses CPU-based enclaves. Here, we decrypt and process the data securely. This keeps it safe from outside access, even from admins or cloud providers.
What is confidentiality in computer security?
Confidentiality ensures that data is only accessible to authorized users. Confidential computing enhances this by securing data while in use.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust is a model that requires strict identity verification for every access attempt, regardless of location or network.
What is Zero Trust in Cyber Security?
In cyber security, Zero Trust means you should not trust any user or device without checking. This helps lower the data security risk of insider threats and lateral attacks.
How to implement Zero Trust Security?
You implement Zero Trust by identifying protect surfaces, using IAM tools, enforcing least privilege, using MFA, and monitoring activity continuously.
How to implement Zero-Trust Security in a network?
Use ZTNA, SDPs, and micro-segmentation. Apply identity validation, endpoint protection, and behavioral monitoring for all network communications.
Conclusion
As digital threats become more sophisticated, businesses must move beyond legacy security models. Confidential Computing and Zero Trust Security are not just buzzwords—they’re the next-generation cybersecurity essentials for data protection.
Using these technologies helps store information safe. This is important for several reasons. You might be working with sensitive financial data. You could be creating AI models. Or you may be managing remote access for many employees. This ensures confidentiality, integrity, and trust in a cloud-first world.
Don’t Wait for a Breach – Explore Trusted Security Now
